Interested in Excavating?
Get Excavating articles, news and videos right in your inbox! Sign up now.
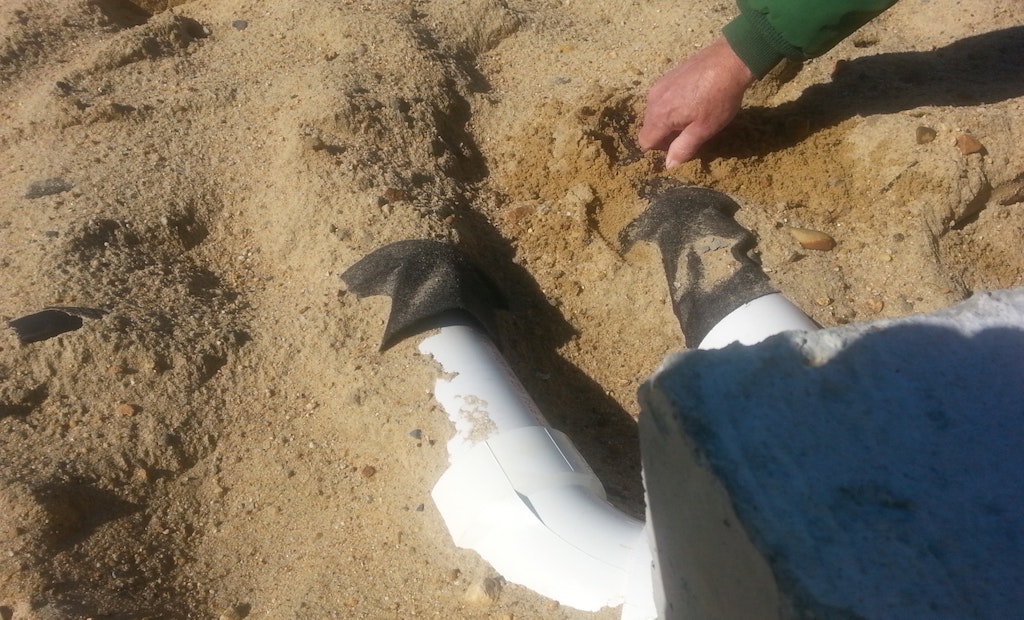
Excavating + Get AlertsProper bedding of system components is critical for level installations. In order for the backfill to serve as a solid base for the component, it should be a material such as pea gravel that does not need to be compacted or it should be installed in lifts and compacted as these layers are installed.
The key issues for selecting a bedding material are:
- Can the material be effectively compacted?
- Is there potential that water will collect in the area the bedding material is being placed?
If water collection is not an issue (particularly with pipe bedding), pea gravel is an appropriate bedding material. In areas where water may collect around components, pea gravel is not appropriate and compactable backfill is needed. Bedding materials are described in the table below.
Bedding Material Specifications
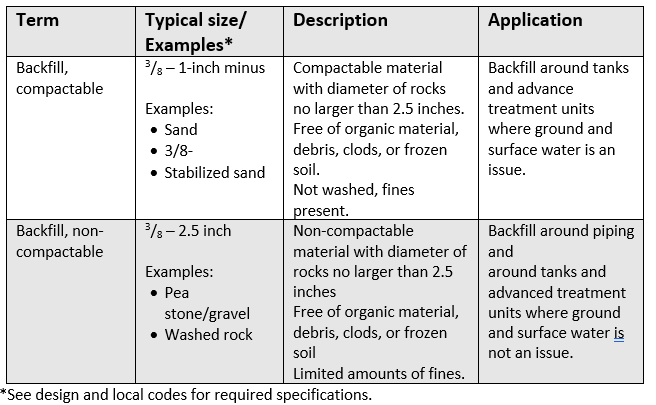
If bedding is necessary, the design should be reviewed to see what material was specified. If none was specified, the installer should consult the designer of the system. Proper bedding of system components is essential for level installations. In order for the backfill to serve as a solid base for the component, it should be a material such as pea gravel that does not need to be compacted, or it should be installed in lifts and compacted as these layers are installed.
Compaction equipment may be needed to achieve the appropriate density when installing pipes and tanks and around modular media filters and aerobic treatment units. A compactor is a machine or mechanism used to reduce the size of the soil void spaces through compaction; they increase the density of the soil. The installer should check with the designer, material provider and/or equipment manufacturer as to the required compaction density.
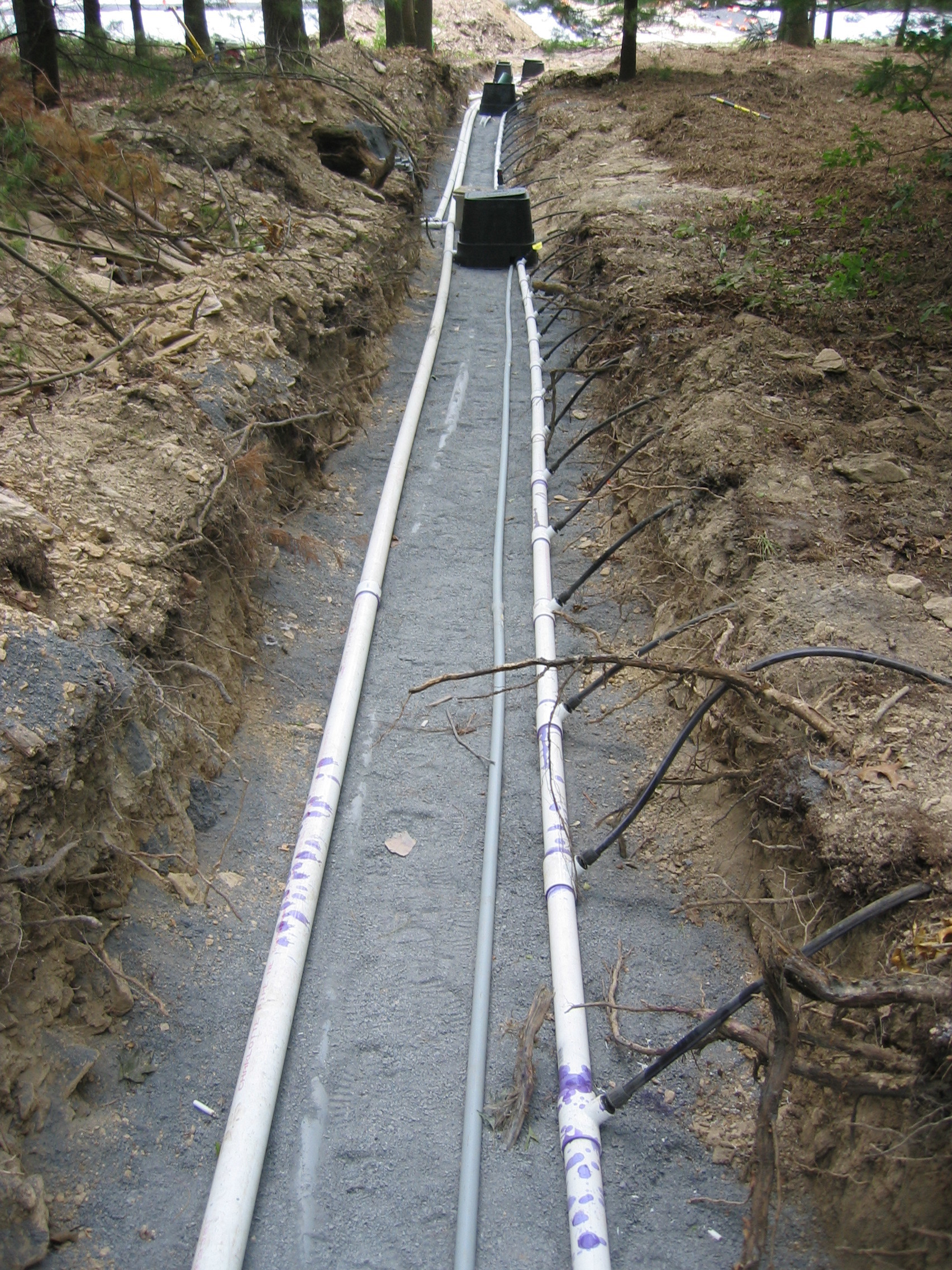

In onsite wastewater treatment system construction, there are two main types of compactors:
- A plate compactor has a large vibrating base plate suited for creating a level grade with granular material and is commonly used to compact the bed of the excavation for a tank.
- A jumping jack has a smaller compaction footprint and is commonly used to compact the backfill in narrow trenches.
A hoe-pack, a compactor that attaches to a backhoe or excavator, should not be used around tanks or advanced treatment components as it may cause structural damage.
Do not use any type of compactor in media filters or on the infiltrative surface or absorption area of any soil treatment area. In media filters, light foot track or watering may be used as needed.
Cover media – soil treatment area backfill
Suitable native soil material to be used for backfill and cover must be free of rocks larger than 2.5 inches in diameter, organic soil, debris, clods or frozen soil. Large clods or frozen soil do not provide a stable cover for the establishment of vegetation. It’s important that this material allow oxygen to get to the soil treatment system, shed surface water, and support the growth of vegetation.
High clay content soils are not recommended as cover material as they have reduced ability to transmit oxygen. High sand content soils are also not recommended as they have low water holding capacity and nutrient levels and therefore do not adequately support the growth of vegetation. Using the correct bedding and cover materials helps to achieve a long-term, sustainable septic system.
About the author
Sara Heger, Ph.D., is a researcher and educator in the Onsite Sewage Treatment Program in the Water Resources Center at the University of Minnesota, where she also earned her degrees in agricultural and biosystems engineering and water resource science. She presents at many local and national training events regarding the design, installation and management of septic systems and related research. Heger is the President of the National Onsite Wastewater Recycling Association and she serves on the NSF International Committee on Wastewater Treatment Systems. Ask Heger questions about septic system design, installation, maintenance and operation by sending an email to kim.peterson@colepublishing.com.






